If you want to learn more about CNNs, Hyperparameters, and RBF neurons, read this article. We will also be discussing Feedforward and CNNs. In the next section we will discuss CNNs. We'll begin with a basic definition for neural networks. Hopefully, this article has been helpful in understanding these concepts. We'll discuss the differences between CNNs and RBF neurons in more detail.
Hyperparameters
The choice and use of hyperparameters within a neural networks is largely an algorithmic decision. The more efficient parallel architectures can use, the larger B. However, the smaller the B, the lower the generalization performance. It is often better to optimize B separately from other hyperparameters. Momentum is an exception. The dataset that is used will dictate the best value of B. It is a good rule of thumb to use a logarithmic scale.
RBF neurons
The RBF neural networks' output layer maps the input and output dimensions. They are the input dimension (or response dimension). RBF neurons are activated when there is a certain weight in the out layer. This weight is multiplied by an undetermined number. The output nodes of each category have their own weights. The weights are normally assigned a value of 0 to the RBF neurons for the category they belong to, and a value of 1 for the rest.
Feedforward networks
Reversibly compressing an input signal is what trains a feedforward neural network. You can input any number of binary numbers from 0-1. The output represents the outcome of the process. This is linear regression. The weights are typically small and random in the range of 0-1. This problem can be illustrated by predicting rain. We can reduce the inputs' weights to 0.1 during training. We can then use the output as our final output.
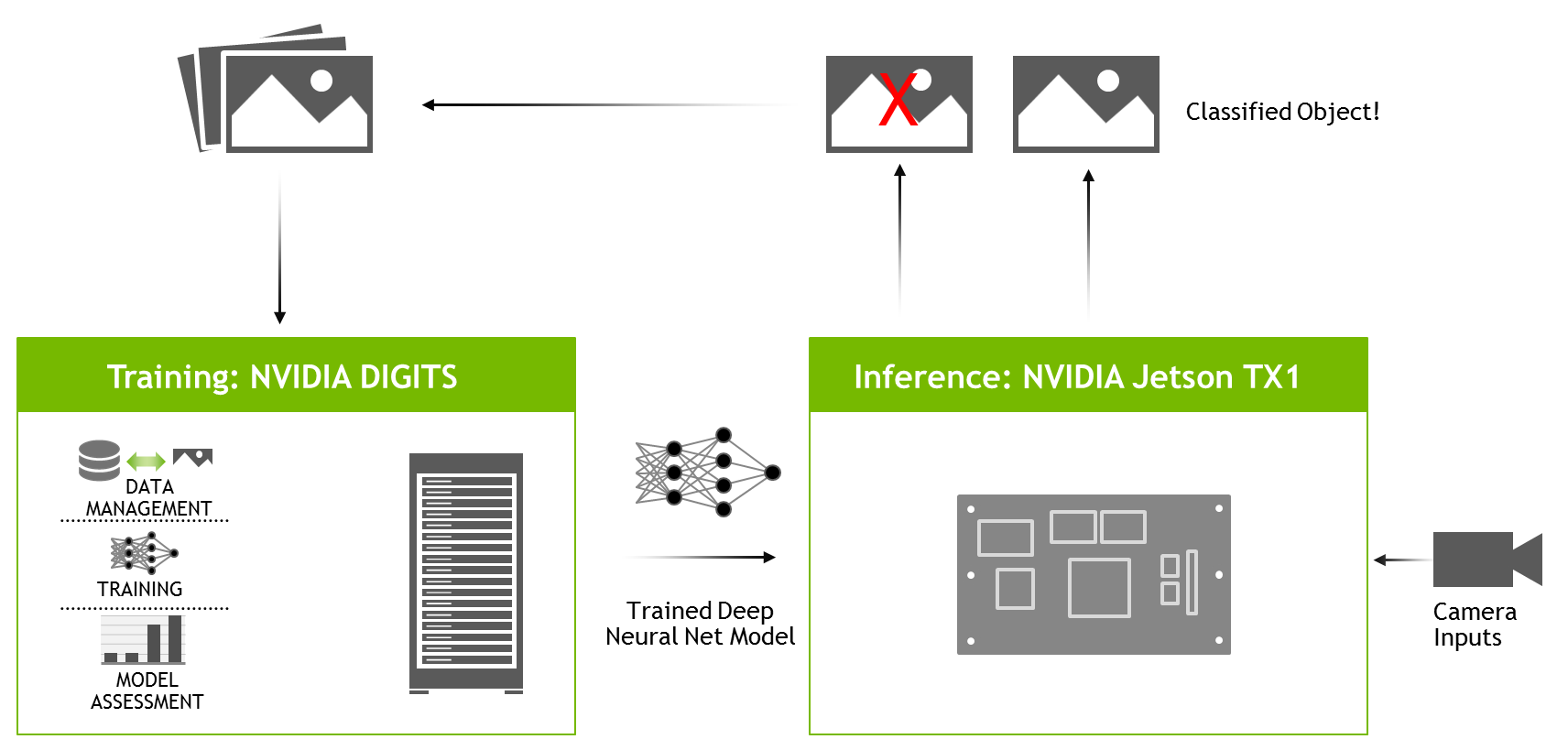
CNNs
CNNs are a form of neural network. They identify objects by comparing features from several sections of an images. The convolution operation is then performed. This is when a patch matrix is multiplied and filtered with learned weights. The output is the class, or likelihood of an object. CNNs are commonly used to classify images. They are also used to identify characters in images. This article will cover the fundamental characteristics of CNNs.
MSMP graph abstraction
MSMP graph abstraction for neural network addresses simplicity and versatility. It removes programming challenges related to GNN mathematical formulation. MSMP graphs depict the entire message-passing process within a GNN. These graphs can also be used to identify relationships between entities. MSMP graphs aid in GNN development by making it more intuitive and productive. This article will discuss both MSMP and GNN graph abstraction.
FAQ
How does AI work?
An algorithm is a set of instructions that tells a computer how to solve a problem. An algorithm can be described as a sequence of steps. Each step has an execution date. The computer executes each instruction in sequence until all conditions are satisfied. This repeats until the final outcome is reached.
Let's say, for instance, you want to find 5. It is possible to write down every number between 1-10, calculate the square root for each and then take the average. However, this isn't practical. You can write the following formula instead:
sqrt(x) x^0.5
You will need to square the input and divide it by 2 before multiplying by 0.5.
The same principle is followed by a computer. It takes your input, squares it, divides by 2, multiplies by 0.5, adds 1, subtracts 1, and finally outputs the answer.
What are some examples of AI applications?
AI is used in many fields, including finance and healthcare, manufacturing, transport, energy, education, law enforcement, defense, and government. Here are just some examples:
-
Finance - AI already helps banks detect fraud. AI can scan millions upon millions of transactions per day to flag suspicious activity.
-
Healthcare – AI helps diagnose and spot cancerous cell, and recommends treatments.
-
Manufacturing – Artificial Intelligence is used in factories for efficiency improvements and cost reductions.
-
Transportation - Self Driving Cars have been successfully demonstrated in California. They are now being trialed across the world.
-
Utilities use AI to monitor patterns of power consumption.
-
Education - AI can be used to teach. Students can, for example, interact with robots using their smartphones.
-
Government - AI can be used within government to track terrorists, criminals, or missing people.
-
Law Enforcement – AI is being used in police investigations. Investigators have the ability to search thousands of hours of CCTV footage in databases.
-
Defense - AI can both be used offensively and defensively. An AI system can be used to hack into enemy systems. Artificial intelligence can also be used defensively to protect military bases from cyberattacks.
Is Alexa an AI?
Yes. But not quite yet.
Amazon has developed Alexa, a cloud-based voice system. It allows users speak to interact with other devices.
The Echo smart speaker was the first to release Alexa's technology. However, similar technologies have been used by other companies to create their own version of Alexa.
These include Google Home and Microsoft's Cortana.
Statistics
- According to the company's website, more than 800 financial firms use AlphaSense, including some Fortune 500 corporations. (builtin.com)
- That's as many of us that have been in that AI space would say, it's about 70 or 80 percent of the work. (finra.org)
- Additionally, keeping in mind the current crisis, the AI is designed in a manner where it reduces the carbon footprint by 20-40%. (analyticsinsight.net)
- A 2021 Pew Research survey revealed that 37 percent of respondents who are more concerned than excited about AI had concerns including job loss, privacy, and AI's potential to “surpass human skills.” (builtin.com)
- More than 70 percent of users claim they book trips on their phones, review travel tips, and research local landmarks and restaurants. (builtin.com)
External Links
How To
How to set Google Home up
Google Home is a digital assistant powered by artificial intelligence. It uses natural language processing and sophisticated algorithms to answer your questions. Google Assistant lets you do everything: search the web, set timers, create reminds, and then have those reminders sent to your mobile phone.
Google Home is compatible with Android phones, iPhones and iPads. You can interact with your Google Account via your smartphone. An iPhone or iPad can be connected to a Google Home via WiFi. This allows you to access features like Apple Pay and Siri Shortcuts. Third-party apps can also be used with Google Home.
Like every Google product, Google Home comes with many useful features. Google Home can remember your routines so it can follow them. It doesn't need to be told how to change the temperature, turn on lights, or play music when you wake up. Instead, you can simply say "Hey Google" and let it know what you'd like done.
These are the steps you need to follow in order to set up Google Home.
-
Turn on your Google Home.
-
Hold the Action button in your Google Home.
-
The Setup Wizard appears.
-
Select Continue.
-
Enter your email adress and password.
-
Choose Sign In
-
Google Home is now online